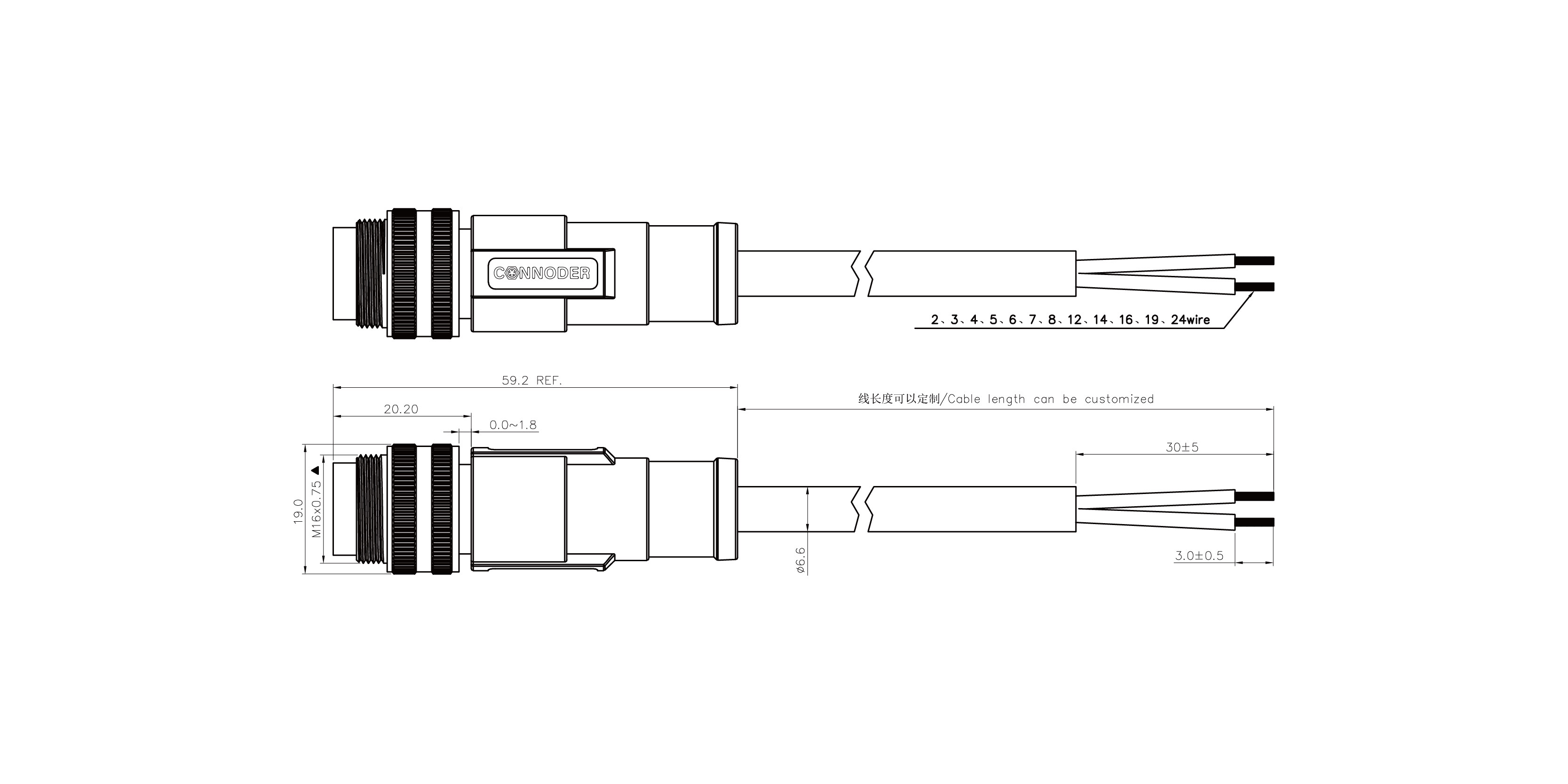
1.1 Selection of conductor materialsConductor is the core part of the cable, and its material directly affects the electrical conductivity and service life of the cable. For most circular connector cables, copper is the material of choice because of its excellent electrical conductivity and good mechanical properties. Aluminum may also be used as an alternative material in some special situations, such as when weight or cost reduction is needed.
1.2 Importance of insulation layer
The main function of the insulation layer is to prevent current leakage and protect the internal conductors from the external environment. Choosing the right insulation material takes into account a number of factors, including operating temperature range, chemical resistance and flexibility. For example, in high temperature environments, silicone rubber or fluoroplastics may be a better choice; Under ordinary conditions, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is enough to meet demand.
1.3 Application of shielding technology
In order to reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference (EMI) on signal quality, many circular connector cables are equipped with shielding layers. Common shielding methods include metal foil wrapping, woven mesh covering, or a combination of both. Effective shielding can not only improve the accuracy of data transmission, but also enhance the overall stability of the system.
1.4 Role of the sheath
As the outermost protective structure of the cable, the sheath plays a key role in resisting physical damage, UV radiation and chemical erosion. Depending on the specific application scenario, different types of sheath materials can be selected, for example, polyurethane (PU) is suitable for high abrasion resistance requirements, while LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) materials are more suitable for places with strict fire safety.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)